Stroke: Support and Education
About 600,000 new strokes are reported in the U.S. each year. The good news is that treatments are available that can greatly reduce the damage caused by a stroke. However, you need to recognize the symptoms of a stroke and get to a hospital quickly. Getting treatment within 60 minutes can prevent disability.
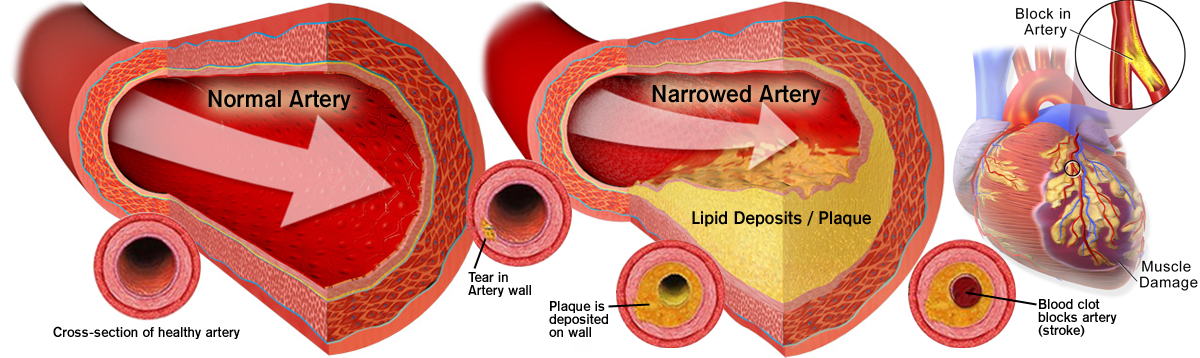
A stroke, or cerebrovascular accident, occurs when the blood supply to the brain is cut off (an ischemic stroke) or when a blood vessel bursts (a hemorrhagic stroke). Without oxygen, brain cells begin to die. Death or permanent disability can result. High blood pressure, smoking, and having had a previous stroke or heart attack increase a person's chances of having a stroke. With timely treatment, the risk of death and disability from stroke can be lowered. It is very important to know the symptoms of a stroke and act right away. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke notes these five major signs of stroke:
- Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arms, or legs.
- Sudden confusion or trouble speaking or understanding others.
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
- Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, or loss of balance or coordination.
- Sudden severe headache with no known cause.
All of the major symptoms of stroke appear suddenly, and often there is more than one symptom at the same time. If you believe someone is having a stroke: if he or she suddenly loses the ability to speak, or move an arm or leg on one side, or experiences facial paralysis on one side - call 911 immediately. Stroke is a medical emergency. Every minute counts when someone is having a stroke. The longer blood flow is cut off to the brain, the greater the damage. Immediate treatment can save people's lives and enhance their chances for successful recovery.
Although stroke is a disease of the brain, it can affect the entire body. The effects of a stroke range from mild to severe and can include paralysis, problems with thinking, problems with speaking, and emotional problems. Patients may also experience pain or numbness after a stroke. Because stroke injures the brain, you may not realize that you are having a stroke. To a bystander, someone having a stroke may just look unaware or confused. Stroke victims have the best chance if someone around them recognizes the symptoms and acts quickly.
Paralysis or loss of muscle movement.
Sometimes, a lack of blood flow to the brain can cause a person to become paralyzed on one side of the body, or lose control of certain muscles, such as those on one side of the face. With physical therapy, you may see improvement in muscle movement or paralysis.
Difficulty talking or swallowing.
A stroke may cause a person to have less control over the way the muscles in the mouth move, making it difficult to talk, swallow or eat. A person may also have difficulty speaking because a stroke has caused aphasia, a condition in which a person has difficulty expressing thoughts through language. Therapy with a speech and language pathologist may improve this disability.
Memory loss or troubles with understanding.
It's common that people who suffer strokes have some memory loss. Others may develop difficulty understanding concepts. This complication may improve with rehabilitation therapies.
Pain.
Some people who have a stroke may have pain, numbness, or other strange sensations in parts of their body affected by stroke. For example, if a stroke causes you to lose feeling in your left arm, you may have an uncomfortable tingling sensation in that arm. You may also be sensitive to temperature changes, especially extreme cold. This is called central stroke pain or central pain syndrome (CPS). This complication may improve with time, but because the pain is caused by a problem in the brain instead of a physical injury, there are few medications to treat CPS.
People who have a stroke may also become withdrawn and less social. They may lose the ability to care for themselves and may need a caretaker to help them with their grooming needs and daily chores after a stroke. As with any brain injury, the success of treating these complications will vary from person to person.
Ischemic strokes, the most common type of strokes, can be treated with a drug called t-PA, that dissolves blood clots obstructing blood flow to the brain. The window of opportunity to start treating stroke patients is three hours, but to be evaluated and receive treatment, patients need to get to the hospital within 60 minutes.
A five-year study by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) found that some stroke patients who received t-PA within three hours of the start of stroke symptoms were at least 30 percent more likely to recover with little or no disability after three months.
Educational programming for healthcare professionals
MEDIVISION ™ collaborates with recognized leaders in the fields of medical and pharmaceutical sciences to provide educational programming for medical specialists, universities and medical schools. Our DVD catalog contains over 200 titles in 35 separate healthcare fields, including a wide variety of specialist topics essential to healthcare professionals.
Cardiovascular programming >